Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine accounts for about a quarter of all cases of osteochondrosis. He is the "youngest" and often affects people under the age of 30. The disease develops gradually, developing slowly but steadily. In the early stages of the development of cervical osteochondrosis, it is generally asymptomatic, becoming an inadvertent finding during X-ray examination
Causes of osteochondrosis
The disease manifests itself as a dull pain in the chest, under the shoulder blades, in the shoulder area, numbness and the appearance of "goose bumps" on the chest, stiffness of movement. Often the pain is girdle in nature, accompanied by angina pectoris, an unpleasant painful sensation in the abdomen, and shortness of breath may occur. Short-term acute pain is sometimes observed.
Causes of vertebral disc destruction and compression of the nerve endings of the spinal cord can be scoliosis acquired in adolescence, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, the same type of load on the spine and regular long -term sitting in a sitting position.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine: symptoms
The most important, first and most frequent symptom of cervical spine osteochondrosis is pain. It gets stronger when bending or turning the head.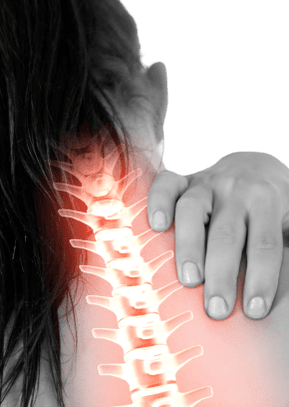 Depending on the localization of the pathological focus, pain can be given to the back of the head, under the scapula or to the arm.
Depending on the localization of the pathological focus, pain can be given to the back of the head, under the scapula or to the arm.
It can be constant, painful. It can occur from time to time, but as the disease progresses, it more often worries a person. The pain was also sharp, shooting. This is a symptom of worsening cervical osteochondrosis, which can manifest itself after hypothermia of the body.
Head movements are usually difficult. This is due to constant muscle tension in the collar and neck zone. While leaning forward or turning the head, irritation is often heard.
In the final stages of cervical osteochondrosis, a person cannot hold his head for long periods of time. Sometimes he couldn’t turn around or tilt it without experiencing severe pain. The patient tries to prop his head with his hands or tries to take a comfortable position to relieve his suffering.
Vertebral artery syndrome

This group of symptoms occurs due to compression of the vertebral arteries by displaced intervertebral discs, oversized cartilage tissue or tense muscles. The syndrome is a complex of symptoms, including cervical migraines, disturbances of consciousness and increased blood pressure.
Cervical migraine is a headache caused by decreased blood flow and lack of oxygen to the tissues. The pain is usually unilateral. Pain, first of all, the back of the head. Possible radiation to ears, eyes or forehead.
Sometimes hearing loss occurs, and the ears start ringing. Possible vision problems. In double eyes, before the eyes "flies flicker. " The scalp can become so painful that it cannot be touched. Headaches with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine are often accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis and frequent compression of the vertebral arteries are an increase in blood pressure. But osteochondrosis of the cervical spine and hypertension are not always interrelated. Keep in mind that in old age, an increase in stress is observed in many people.
Only after reviewing the history of cervical osteochondrosis, the doctor can determine whether hypertension is a complication of the disease. If there is a history of recurrent arterial hypertension attacks, which are accompanied by palpitations and fear of death, most likely this is one of the symptoms of vertebral artery compression. If the increase in pressure occurs gradually and frequent hypertensive crises are not observed, most likely, the patient has hypertension, which is not related to osteochondrosis.
Damage to consciousness occurs when the blood supply to the brain is insufficient. There is a feeling of drowsiness, dizziness, decreased speed of reaction to external stimuli. Short -term loss of consciousness occurs.
Recovery after spinal stroke
What are the most dangerous symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis? Without a doubt, this is a spinal stroke - the death of part of the spinal cord due to the complete absence of blood flow in the squeezed duct. Always leads to disability, causing paresis and paralysis. Fortunately, spinal strokes are rare.
Heart syndrome
Among the symptoms of worsening osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, there is heart pain. It occurs due to pinching of the posterior root of the fourth spinal cord. In fact, heart pain can be associated with radicular syndrome. But these symptoms are specific and therefore isolated as a separate syndrome.
Heart disease with osteochondrosis can mimic angina pectoris or myocardial infarction. But when a patient seeks medical help, immediately a competent doctor, based only on the patient's symptoms and complaints, can rule out heart disease.
- First, the presence of other symptoms of cervical vertebral osteochondrosis in a patient will cause the specialist to know that the cause of heart disease can be a problem in the spine;
- Second, the pain is not strong and sharp, as in myocardial infarction, and is not accompanied by fear of death. It is not associated with physical activity, in contrast to angina pectoris attacks;
- Third, such pain is long enough and after taking nitroglycerin, it will not disappear and does not even subside;
- Fourth, pain is increased by turning or tilting the head, which is not observed with "real" heart disease.
Radicular syndrome
Radicular syndrome combines signs of cervical osteochondrosis that develop as a result of compression of the spinal nerve roots. Depending on the stage at which the pinch occurs, various symptoms of cervical spine intervertebral osteochondrosis can develop.
Root compression at the level of the first or second segment leads to numbness in the occipital skin or pain in the occipital area.
Pinching the third spinal nerve root causes numbness of the tongue and skin behind the ears. If the motor fibers are pinched, it is difficult for a person to chew food and he feels his tongue grow.
Root compression at the level of the fourth segment of the spinal cord causes pain in the heart and collarbone, hiccups and pharyngeal migraines. There is a sensation of foreign objects in the throat, it is difficult to swallow food. There may be a sore throat that mimics a sore throat. But the differential diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis and tonsillitis is not at all difficult. Inflammation of the pharyngeal tonsils is always accompanied by hyperthermia, whereas with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, the body temperature does not rise.
Symptoms for cervical osteochondrosis
The most common symptom of pinching the root of the fifth spinal cord is a movement disorder of the shoulder muscles. It is difficult for the patient to raise his hand and bring it to the side.
Pinching the root of the sixth segment most often causes pain in the scapula and forearm. It becomes difficult for the patient to bend and twist the forearm.
The seventh pair of spinal nerves primarily turn the hand, index and middle fingers. When pinched, the movement of these body parts is disrupted, numbness or pain occurs.
Pinching at the level of the eighth segment makes it difficult to bend and lengthen the ring finger and little finger. Pain and sensory disturbances may also occur. However, this manifestation can already be associated with symptoms of cervical spine osteochondrosis, because the nerve root of the eighth spinal cord is located between the seventh cervix and the first thoracic vertebra.
What are the dangers of cervical osteochondrosis? First of all, by its complications. The appearance of an intervertebral hernia can lead to spinal cord compression and, as a consequence, the development of paresis and paralysis. When the first symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis appear, treatment should be started. Properly selected therapy will slow the progression of the disease, improve the patient’s quality of life, and prevent the development of complications of cervical osteochondrosis.